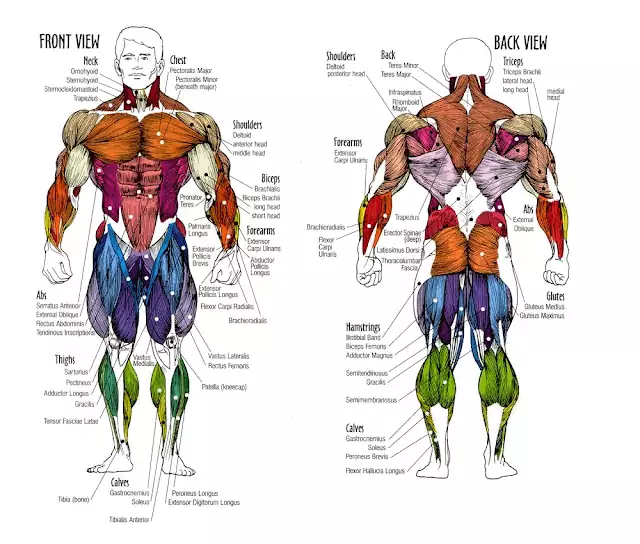
Knowing where your quadriceps are is a good start but that doesn’t necessarily mean you understand anatomy. However, once you understand what insertions of origins are, in other words the points where muscles attach to the bone, you are well on your way to understanding some of the basic biomechanics of the body.
The agonist and antagonist muscles can help you understand which muscles oppose each other and how to compensate for muscle imbalance. The agonist is the prime mover, the muscle or muscles creating movement. On the other hand, the antagonist is the muscle, or muscles, opposing that movement. For example, the hip extensors, including the hamstrings, are the agonists while the antagonists (the ones that elongate) are the hip flexors, including the rectus femoris. As a general rule, antagonists elongate and prime movers contract.
The Abdominal Muscles
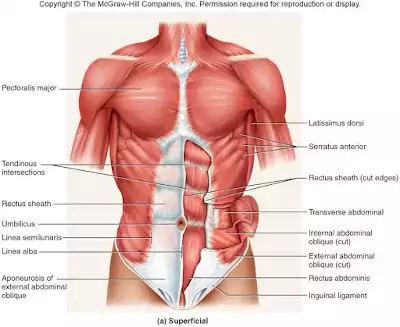
The abdominal area comprises the rectus abdominis, which extends along the length of the abdomen and the external obliques which are at the side of the torso. These abdomen muscles help pull the upper and lower body together so the organs are always aligned in their proper place. Well developed abs help give that lean and fit look.
The Shoulder Muscles
The shoulder muscles are the deltoid and the trapezius. Their function is to rotate and lift the arm. Well developed shoulder muscles add to a person’s stature and help give a large and muscular impression.
The Arm Muscles
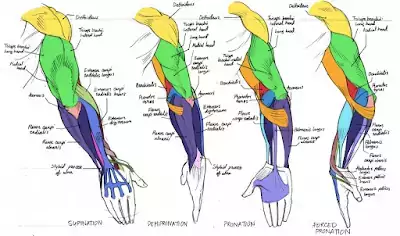
These are the biceps, triceps and forearms. The main function of the bicep is to lift and curl the arm while the tricep is designed to straighten and twist up the arm. The the basic function of the forearm is to curl the palm forward and pull the hand backwards.
The Chest Muscles
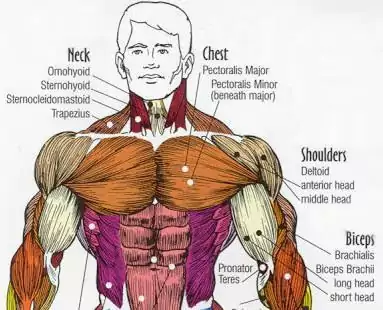
The pectorals are your chest muscles, the large fan-shaped muscles covering the rib cage area. Their function is to pull the arm and shoulder in front of the body. The other muscle is the subclavicus, a cylindrical muscle that helps draw the muscle forward.
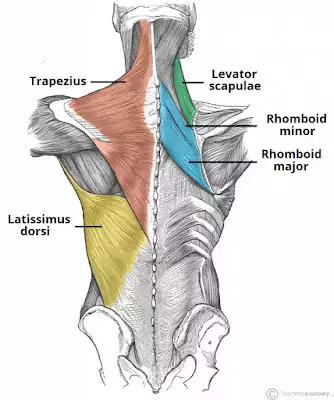
The Back Muscles
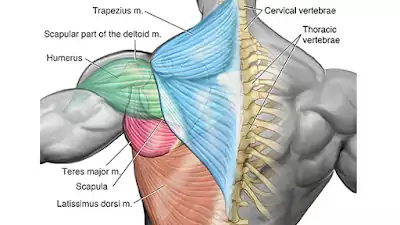
The back muscles are composed of the trapezius (or traps), the triangular muscle that helps raise the entire shoulder girth, the latissmus dorsi (or lats), another triangular muscle that helps pull the shoulder down and back, and finally, the spinal erectors which are several muscles in the lower back that cover the nerves and keep the spine erect.
The Leg Muscles
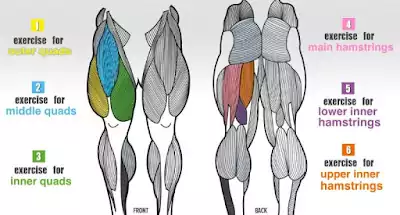
The leg muscles comprise the quadriceps at the front of the thigh which extend down the leg. The four quadriceps muscles are the rectus femoris, the vastus intermedium, the vastus medialis and the vastus lateralis. The calf muscles comprise the soleus which is the larger muscle and used to flex the foot and the double-headed gastrocnemius, which also flexes the foot.